External Anatomy

Abdomen: posterior body segment from which the spinnerets come out of, houses majority of internal organs
Spinnerets: silk-producing appendages extending from the rear, silk used for draglines and nest-making (not catching prey)
Prosoma or cephalothorax: anterior body segment which houses mouth, eyes, and appendages, covered by shell or carapace
Carapace: single plate or shell (exoskeleton) that covers prosoma
Chelicerae: jaws on the front of the prosoma that house hollowed out fangs through which venom is injected into prey, also contain digestive fluids
Pedipalp or Palpi: group of paired appendages proximal to the chelicerae that are used as sensory appendages and oftentimes in reproduction
Eyes: group of eight very sophisticated eyes that are used for hunting prey, capable of magnifying, focusing, discerning color, and processing visual images
Spinnerets: silk-producing appendages extending from the rear, silk used for draglines and nest-making (not catching prey)
Prosoma or cephalothorax: anterior body segment which houses mouth, eyes, and appendages, covered by shell or carapace
Carapace: single plate or shell (exoskeleton) that covers prosoma
Chelicerae: jaws on the front of the prosoma that house hollowed out fangs through which venom is injected into prey, also contain digestive fluids
Pedipalp or Palpi: group of paired appendages proximal to the chelicerae that are used as sensory appendages and oftentimes in reproduction
Eyes: group of eight very sophisticated eyes that are used for hunting prey, capable of magnifying, focusing, discerning color, and processing visual images
Internal Anatomy (cross section of spider)
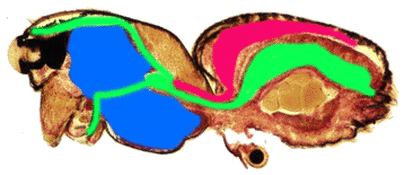
Digestive System in Green, Brain in Blue, Heart in Red
Pharynx: shovel-like organ that transports food from mouth to esophagus
Esophagus: brings food from pharynx to the sucking stomach, transversing through the middle of the brain in the process
Sucking Stomach: site of food digestion, system branches out to appendages from the site of the stomach to transport food to appendages and the rest of the body
Brain: very large processing organ which controls body functions
Heart: proportionately large pumping organ that consists of a single tube that pumps hemolymph to the rest of the body (open circulatory system)
Tracheae: tubules that are open to the outside and extend throughout the body cavity, take in air and oxygen is diffused into the blood
Book Lungs: primitive respiratory lung that contains hemolymph and provides site for oxygen exchange
